Publication
-
New Publicaion from Eisenhauer et al. in Basic and Applied Ecology: The multiple-mechanisms hypothesis of biodiversity–stability relationships
Long-term research in grassland biodiversity experiments has provided empirical evidence that ecological and evolutionary processes are intertwined in determining both biodiversity–ecosystem functioning (BEF) and biodiversity–stability relationships. Focusing on plant diversity,…
-
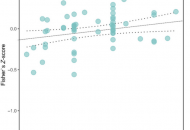
New Publicaion from Lipoma et al. in Global Ecology & Biogeography: No general support for functional diversity enhancing resilience across terrestrial plant communities
Aim Understanding the mechanisms promoting resilience in plant communities is crucial in times of increasing disturbance and global environmental change. Here, we present the first meta-analysis evaluating the relationship between…
-
New Publication from de Souza in FEMS Microbiology Ecology: The effect of successive summer drought periods on bacterial diversity along a plant species richness gradient
Drought is a major stressor to soil microbial communities, and the intensification of climate change is predicted to increase hydric stress worldwide in the coming decades. As a possible mitigating…
-
New publication from Cheng et al. in Nature Communications: Biodiversity increases resistance of grasslands against plant invasions under multiple environmental changes
Biodiversity often helps communities resist invasion. However, it is unclear whether this diversity–invasion relationship holds true under environmental changes. Here, we conduct a meta-analysis of 1010 observations from 25 grassland…
-
New publication from Eisenhauer et al. in Research Ideas and Outcomes: Plant diversity effects on soil multistability
Soil is the basis for life on Earth as we know it. Healthy and stable soil is a prerequisite for well-functioning terrestrial ecosystems and has, thus, been proposed to play…
-
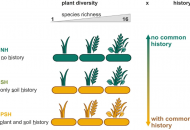
New publication from Albracht et al. in Biology and Fertility of Soils: Common soil history is more important than plant history for arbuscular mycorrhizal community assembly in an experimental grassland diversity gradient
The relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning strengthens with ecosystem age. However, the interplay between the plant diversity – ecosystem functioning relationship and Glomeromycotinian arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) community assembly…
-
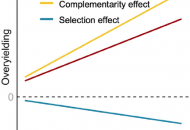
New publication from He et al. in Communications Biology: Cumulative nitrogen enrichment alters the drivers of grassland overyielding
Effects of plant diversity on grassland productivity, or overyielding, are found to be robust to nutrient enrichment. However, the impact of cumulative nitrogen (N) addition (total N added over time)…
-
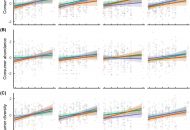
New publication from Bröcher et al. in Basic and Applied Ecology: The positive plant diversity/consumer relationship is independent of grassland age
Plant diversity is an important driver of many ecosystem processes within and among trophic levels. There is growing evidence that the strength of plant diversity effects depends on the biotic…
-
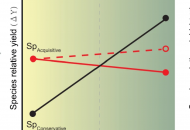
New publication from Zheng et al. in Nature Communications: Effects of plant diversity on productivity strengthen over time due to trait-dependent shifts in species overyielding
Plant diversity effects on community productivity often increase over time. Whether the strengthening of diversity effects is caused by temporal shifts in species-level overyielding (i.e., higher species-level productivity in diverse…
-
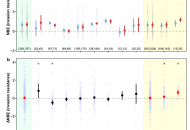
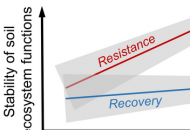
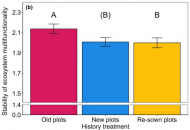
New publication from Dietrich et al. in Global Change Biology: Plant diversity and community age stabilize ecosystem multifunctionality
It is well known that biodiversity positively affects ecosystem functioning, leading to enhanced ecosystem stability. However, this knowledge is mainly based on analyses using single ecosystem functions, while studies focusing…
Posts navigation
We’ve made the move from Twitter to Bluesky. Follow us there for all the latest updates.