Featured
-
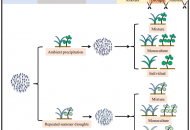
New publication from Chen et al. in Nature Communications: Drought-exposure history increases complementarity between plant species in response to a subsequent drought
Drought-exposure history increases complementarity between plant species in response to a subsequent drought Growing threats from extreme climatic events and biodiversity loss have raised concerns about their interactive consequences for…
-
New publication from Schmid et al. in Grassland Research: Removing subordinate species in a biodiversity experiment to mimic observational field studies
Positive effects of plant species richness on community biomass in biodiversity experiments are often stronger than those from observational field studies. This may be because experiments are initiated with randomly…
-
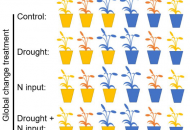
New publication from Dietrich et al. in eLife: Eco-evolutionary dynamics modulate plant responses to global change depending on plant diversity and species identity
Global change has dramatic impacts on grassland diversity. However, little is known about how fast species can adapt to diversity loss and how this affects their responses to global change.…
-
New publication from Guimarães-Steinicke et al. in Remote Sensing: Diversity Effects on Canopy Structure Change throughout a Growing Season in Experimental Grassland Communities
Increasing plant diversity commonly enhances standing biomass and other ecosystem functions (i.e., carbon fluxes, water use efficiency, herbivory). The standing biomass is correlated with vegetation volume, which describes plant biomass…
-
Master thesis on the role of intraspecific chemical plant variation on associated arthropod food web structure (Jena, Germany)
To what extent chemical profiles and chemical diversity of the basal resource (tansy) determine food web dynamics and structure aphid metacommunities. Background: At an intraspecific level, phenotypic differences can be…
-
Wir suchen Verstärkung (m/w/d) für ein 5-wöchiges Projekt auf den Biodiversitä-tsflächen in Jena vom 7. März bis zum 8. April 2022
Umwelt-Geräte-Technik GmbH Deine Aufgaben: Unterstützung beim Stechen von Bodenmonolithen mit 500 mm Durchmesser Umrüsten der hydraulischen Stechvorrichtung, keine Angst, sie beißt nicht Abdichten und Konfektionieren von Lysimetergefäßen mit Saugkerzenringen Verfüllen…
-
New publication from Eisenhauer et al. in Science China Life Sciences: The shape that matters: how important is biodiversity for ecosystem functioning?
This article summarized the history and current biodiversity-ecosystem functioning research. It shows that lately study by Bongers et al. 2021 contributes a significant aspect to this field of research. It…
-
New publication from Eisenhauer et al. in Science: Ecosystem effects of environmental extremes
Climate and biodiversity change influence carbon, water, and greenhouse gas dynamics, thereby driving the delicate balance of ecosystems as carbon sinks or sources. On page 1514 of this issue, Werner…
-
New publication from Schielzeth et al. in American Journal of Botany: Community genomics: a community-wide perspective on within-species genetic diversity
It is increasingly being recognized that diversity within species constitutes another important component of biodiversity with consequences for ecosystem functioning (Raffard et al., 2019; Stange et al., 2021). Intraspecific genetic variation provides…
-
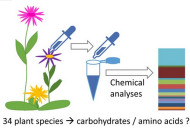
New publication from Venjakob et al. in Plant Biology: Variation in nectar quality across 34 grassland plant species
Floral nectar is considered the most important floral reward for attracting pollinators. It contains large amounts of carbohydrates besides variable concentrations of amino acids and thus represents an important food…
Posts navigation
We’ve made the move from Twitter to Bluesky. Follow us there for all the latest updates.